Zomato a global restaurant discovery and food delivery platform founded by Deepinder Goyal along with Pankaj Chaddah in year 2008 became one of the most valuable company from the Indian startup ecosystem with a market capitalisation of $15.29 billion.
Initially started with the name Foodiebay in July 2008, the idea was sparked when Deepinder Goyal, after his graduation from IIT Delhi Joined Bain and Company as a Senior associate consultant noticed long queues for menu cards in their office cafeteria at Bain. This led him to digitize menus and make them accessible online.
Deepinder Goyal today has a whooping net worth of 2030 crores Indian rupees with the company having market share of 55% in food delivery industry.
Rebranding and Going Global–
In 2010, Foodiebay was rebranded as Zomato to avoid confusion with eBay and also expanded its services to major Indian cities like Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, Pune, and Hyderabad.
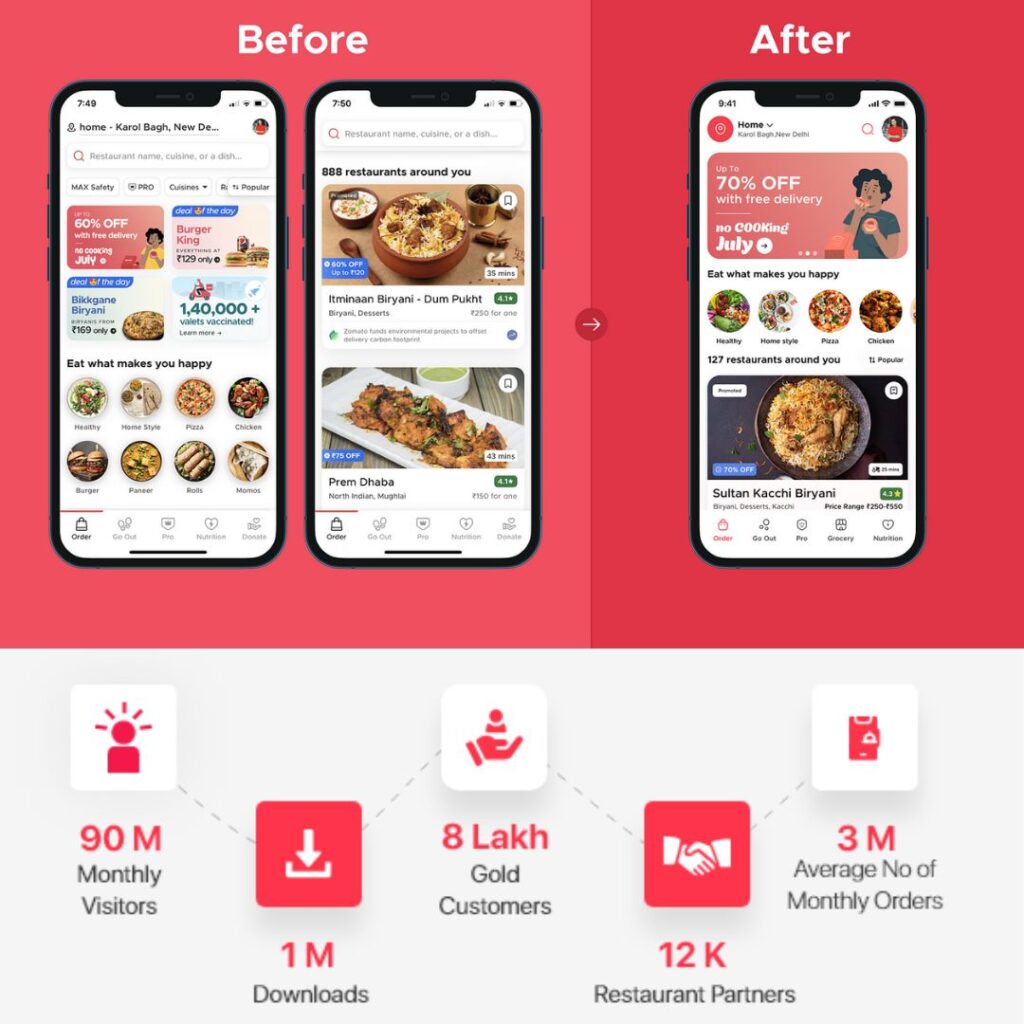
They also improvised on their app’s interface making it more user friendly.
Between 2011-2013, Zomato launched its services in Dubai, UAE, marking its first international venture.
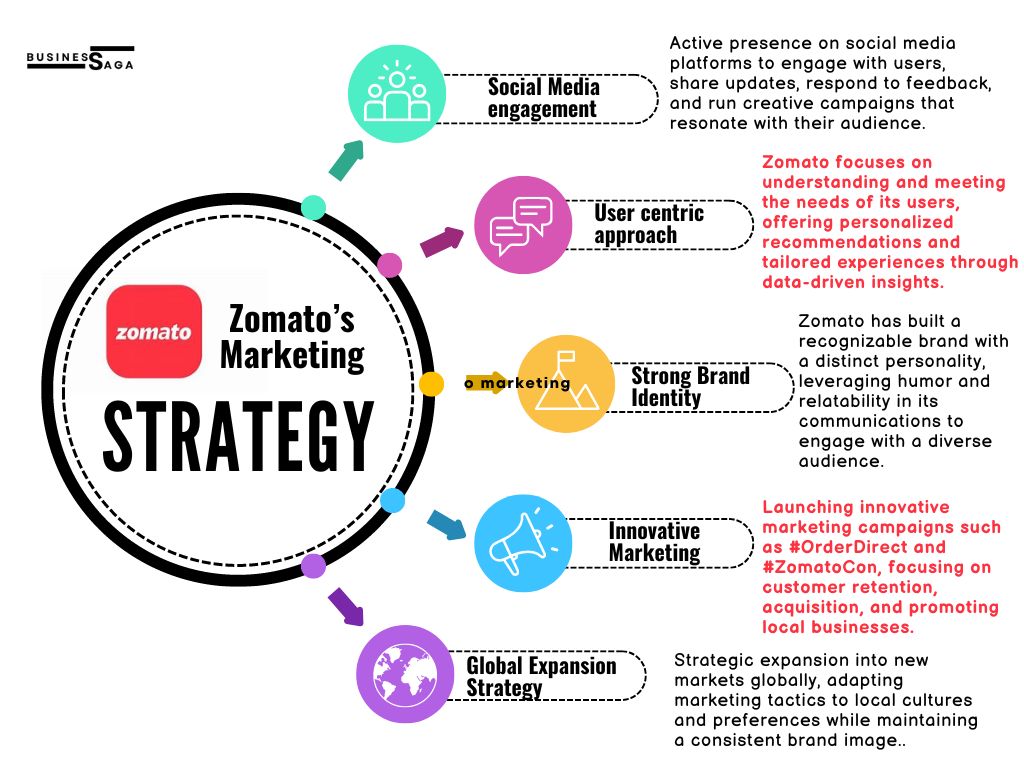
Zomato’s Marketing Strategy:
Zomato’s innovative marketing strategy has yielded impressive results, solidifying its position as a leader in the food delivery industry. By leveraging social media engagement, strategic partnerships, and data-driven insights, Zomato has significantly increased user acquisition and retention. Creative campaigns and a strong brand identity have enhanced customer loyalty, while global expansion efforts have widened its market presence.
Zomato Revenue Model:
Zomato is known for its marketing strategies and holds one of the most successful revenue models in startup ecosystem. This helped the company again set a comeback, marking a profitability in year 2023.
1.Commission on Food Orders:
Zomato charges a commission to restaurants on each order placed through its platform.
2.Advertising:
Restaurants can pay to advertise on Zomato’s platform, gaining better visibility through featured listings, banners, and other promotional placements.
3.Subscription Services and Delivery Charges:
Zomato Pro and Pro plus, a subscription-based service offering members exclusive discounts and deals at partner restaurants. Also users are charged a delivery fee on food orders, which contributes to revenue.

4.White-Label Access:
Zomato provides technology solutions to restaurants, including POS systems, reservation systems, and white-label apps. Restaurants pay for access to these tools.
5.Grocery Delivery:
Although primarily focused on food delivery, Zomato has ventured into grocery delivery, charging a commission on each sale.
During the fiscal year ending in March 2023, Zomato reported a significant increase in revenue, reaching approximately $1.2 billion USD, marking a substantial growth from previous years.
This growth was fueled by their expansion into new markets, innovative offerings like hyperpure and cloud kitchens, and effective cost management strategies. Coupled with aggressive marketing campaigns that emphasized user engagement and brand loyalty, Zomato successfully navigated challenges and emerged stronger, reaffirming its position as a leader in the global food delivery and restaurant discovery industry.